In today’s digital landscape, understanding how customers interact with brands is more critical than ever. The journey from awareness to conversion is rarely linear, and marketers are tasked with decoding this complex path. This is where attribution models come into play, providing insights into how different touchpoints influence customer behavior.
What is Attribution?
Attribution refers to the process of assigning credit to various marketing channels for their role in the customer journey. When a customer interacts with multiple touchpoints—be it digital ads, social media, email campaigns, or organic search—attribution models help determine which channels are most effective in driving conversions.
The need for strong attribution models arises from the fact that today’s customers engage with brands across various platforms, often multiple times, before making a purchase. Understanding this interaction can help brands allocate resources more effectively and enhance future marketing strategies.
Why Attribution Matters
1. Resource Allocation: With limited marketing budgets, determining which channels yield the highest return on investment (ROI) is critical. Attribution models help identify the most effective touchpoints, allowing marketers to allocate resources strategically.
2. Strategy Optimization: Understanding how customers engage with different channels enables marketers to tailor their strategies accordingly. For example, if email campaigns are driving more conversions than social media, marketers can emphasize email marketing efforts.
3. Customer Experience: By analyzing the customer journey, brands can improve the overall customer experience. The insights gained from attribution can help streamline the path to purchase, making it smoother and more intuitive for customers.
Types of Attribution Models
Attribution models can be categorized into several types, each providing a different perspective on how to evaluate customer interactions:
1. First-Click Attribution
In this model, all credit for a conversion is given to the first interaction a customer has with a brand. This approach is useful for understanding how customers discover a brand but fails to account for subsequent touchpoints that may also have influenced the final decision.
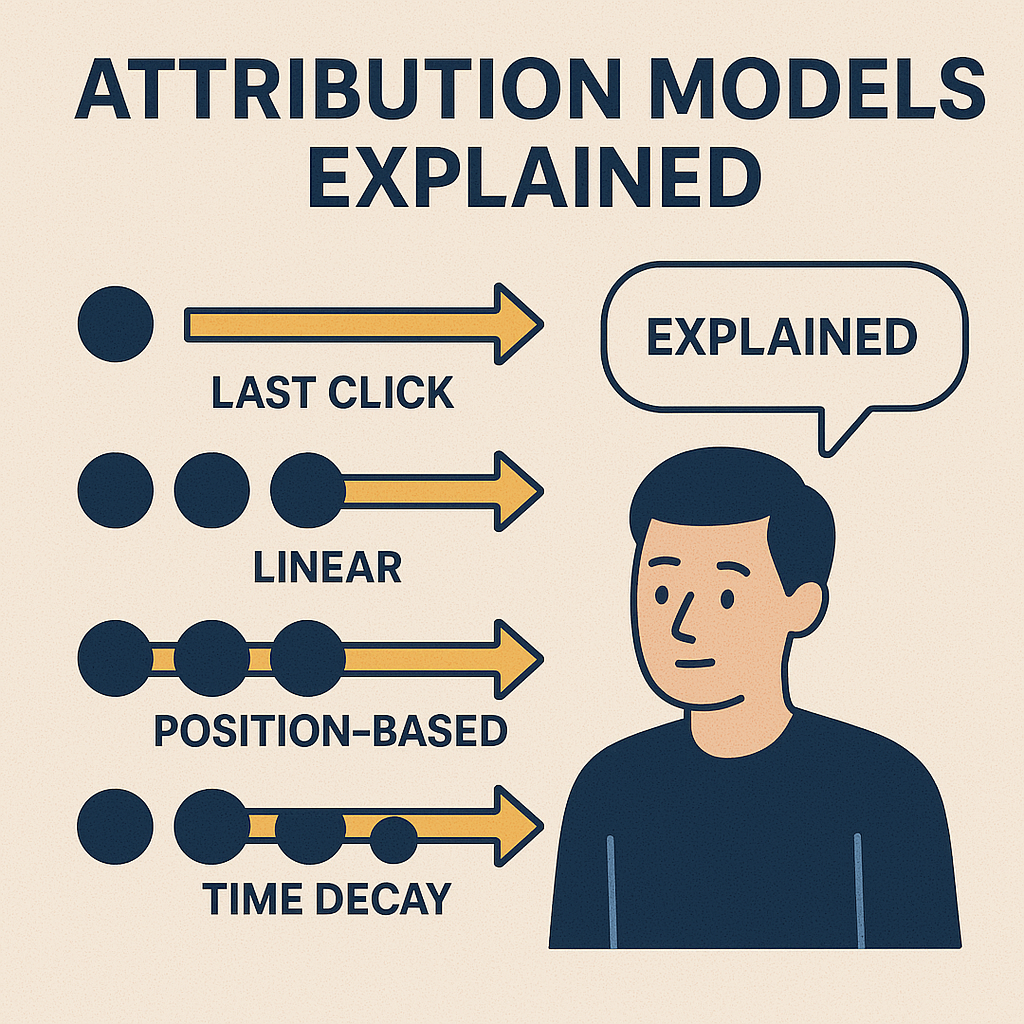
2. Last-Click Attribution
The Last-Click attribution model gives complete credit to the last interaction before conversion. While it highlights the final nudge that convinced the customer to make a purchase, it neglects the role of earlier touchpoints in the journey.
3. Linear Attribution
Linear attribution distributes credit equally across all touchpoints in the customer journey. This model acknowledges that each interaction plays a role but may oversimplify the complex nature of consumer decision-making.
4. Time-Decay Attribution
This model assigns more credit to the touchpoints closer to the conversion, gradually decreasing the credit of earlier interactions. This approach provides insight into the importance of recent engagements leading up to the decision.
5. Position-Based Attribution
Also known as U-shaped attribution, this model allocates 40% of the credit to both the first and last interactions, with the remaining 20% spread evenly across the middle interactions. This emphasizes the importance of both initial engagement and the final push.
6. Data-Driven Attribution
The most advanced model uses data analytics to assess the value of each touchpoint based on its actual contribution to conversions. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, brands can get a more accurate picture of customer behavior, allowing for precise adjustments to marketing strategies.
Choosing the Right Model
Selecting the right attribution model depends on several factors:
- Business Goals: If the goal is to improve brand awareness, a first-touch model may be more appropriate. On the other hand, if the focus is on conversions, last-touch or time-decay models could provide better insights.
- Customer Journey Complexity: For brands with lengthy and complex customer journeys, data-driven or position-based models might be more effective.
- Data Availability: The choice of model will also depend on the data available. Brands with robust analytics capabilities can benefit from data-driven attribution models.
Conclusion
Attribution models are vital for uncovering the intricacies of the customer journey. By providing clarity on how different touchpoints interact, these models empower marketers to make informed decisions that can significantly enhance their approach. As the landscape evolves, brands need to continually assess and adapt their attribution strategies to ensure that they not only understand but effectively respond to the behaviors and preferences of their customers.
Understanding attribution is not just about measuring success—it’s about deciphering the customer journey to create a more personalized and impactful brand experience. By embracing these models, businesses can decode the complexities of journey and lay the groundwork for lasting customer relationships.